NeuralQA Documentation¶
NeuralQA provides an easy to use api and visual interface for Question Answering (QA),
on large datasets. The QA process is comprised of two main stages - Passage retrieval (Retriever) which is implemented using ElasticSearch
and Document Reading (Reader) which is implemented using pretrained BERT models via the
Huggingface Transformers api.
You can install it via pip:
pip3 install neuralqa
Launch the web interface via command line:
neuralqa ui --port 5000
You can also clone this repository, make changes and launch the application directly from repository:
python neuralqa/cli.py ui
Why NeuralQA?¶
The goal of NeuralQA is to provide the quickest path to exploring QA with as little changes as possible to your current infrastructure.
NeuralQA is helpful in a few ways:
A visual interface for sensemaking of model results.
A rest api for QA related operations (retrieval, document reading, model explanation).
Helpful implementations that can improve the QA process - RelSnip (Relevant Snippets): The content of retrieved documents can be lengthy, incurring high latency costs for a docuement reader to process the entire document. RelSnip constructs a smaller passage by concatenating subsections of the original documents that contain exact keyword matches for the query. This set of relevant snippets is then processed by the document reader. - Query expansion: Sparse representation retrievers like BM25 and TFIDF (implemented in ElasticSearch) rely on exact query keyword matching. This can be problematic if a different vocabulary is used in the documents to express the same content. To help address this, NeuralQA can rewrite the query to integrate additional keywords to increase the set of relevant retrieved documents.
Configurable via a yaml configuration file.
Bring your own QA reader. You can select from the gallery of QA models provided by HuggingFace or provide your own finetuned HuggingFace model.
Bring your own retriever. You can attach NeuralQA to an existing retriever instance (elasticsearch) and configure retriever queries.
Configure the visual interface.
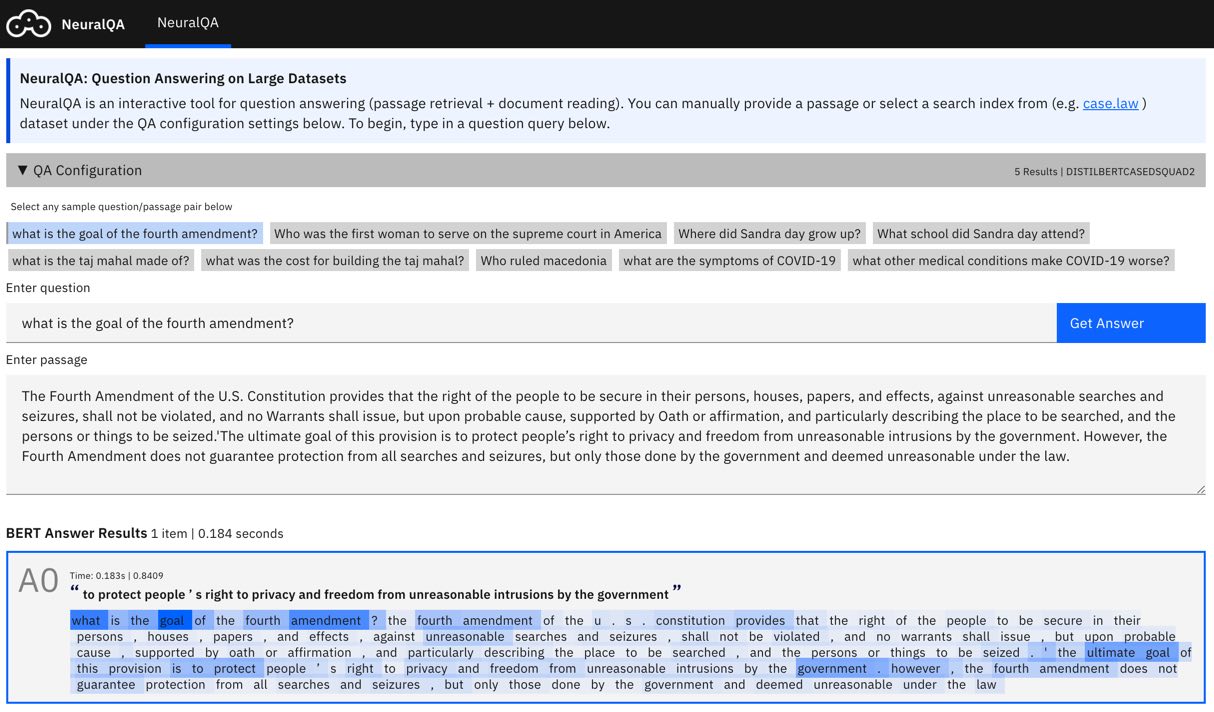
Show/hide views: e.g. show/hide retrieved passages, show only top answer or all answers, show sample questions etc.
Show/hide controls: e.g. show/hide controls for selected retriever, reader etc.
Content: You can rename the title and descriptions as needed.
NeuralQA is created to be helpful for two groups of users:
Hobbyists: Try out QA models on your own data or retriever setup and visually inspect the results.
Teams: Provide a front facing QA interface for your end users on your retriever instances. You can create docker containers that run NeuralQA for scale and configure them with your retriever instance clusters.
How It Works¶
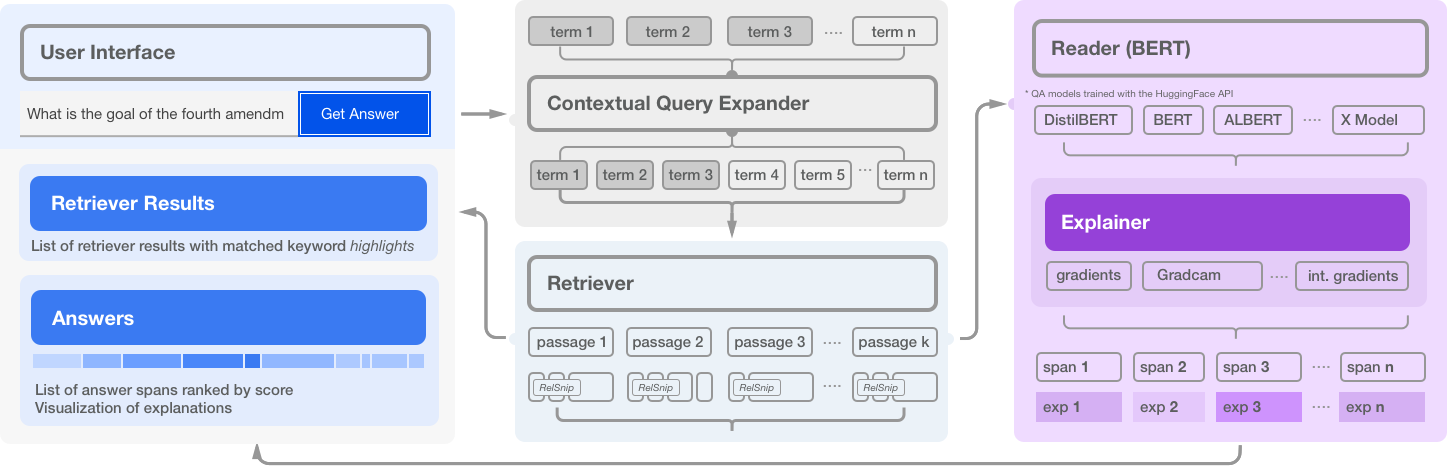
NeuralQA is comprised of several high level modules:
Retriever: For each search query (question), scan an index (elasticsearch), and retrieve a list of candidate matched passages.
Reader: For each retrieved passage, a BERT based model predicts a span that contains the answer to the question. In practice, retrieved passages may be lengthy and BERT based models can process a maximum of 512 tokens at a time. NeuralQA handles this in two ways. Lengthy passages are chunked into smaller sections with a configurable stride. Secondly, NeuralQA offers the option of extracting a subset of relevant snippets (RelSnip) which a BERT reader can then scan to find answers. Relevant snippets are portions of the retrieved document that contain exact match results for the search query.
Expander: Methods for generating additional (relevant) query terms to improve recall. Currently, we implement Contextual Query Expansion using finetuned Masked Language Models.
User Interface: NeuralQA provides a visual user interface for performing queries (manual queries where question and context are provided as well as queries over a search index), viewing results and also sensemaking of results (reranking of passages based on answer scores, highlighting keyword match, model explanations).
Citation¶
A paper introducing NeuralQA and its components can be found here.
@article{dibia2020neuralqa,
title={NeuralQA: A Usable Library for Question Answering (Contextual Query Expansion + BERT) on Large Datasets},
author={Victor Dibia},
year={2020},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.15211}
}